Written by Microscopehunt Authority
.
Compound Microscope vs. Stereo Microscope:
Microscopes are essential tools in laboratories, classrooms, and research various types, the compound microscope and the stereo microscope are the facilities, allowing us to explore tiny details of the world around us. Among the most commonly used. This article will help you understand the key differences between these two types and guide you on which one to choose for your needs.
What is a Compound Microscope?
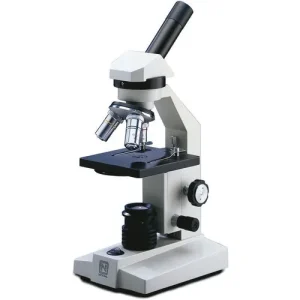
A compound microscope employs several lenses to enlarge small specimens for better observation. It typically consists of an objective lens and an eyepiece lens, which work together to provide high magnification. Compound microscopes are designed for viewing thin samples, like cells or tissues, that light can pass through. They are widely used in biology and medical laboratories for studying intricate details.
What is a Stereo Microscope?
A stereo microscope, also known as a dissecting microscope, provides a three-dimensional view of larger, opaque specimens. Unlike the compound microscope, it uses two separate optical paths to create depth perception. This type of microscope is excellent for examining surfaces of objects, such as insects, plants, or mechanical parts. Stereo microscopes are often used in fields such as entomology, botany, and electronics.
Main Differences Between the Two Microscope Types
The key difference between a compound microscope and a stereo microscope lies in their design and functionality. Compound microscopes are designed for high magnification of thin, transparent specimens, allowing detailed examination of cellular structures. In contrast, stereo microscopes provide lower magnification but offer a three-dimensional view, making them ideal for larger, opaque specimens.
Ideal Specimens for Compound Microscopes
Compound microscopes excel at examining small, thin specimens that light can easily pass through. Examples of suitable samples include:
Biological Samples:
Cells, tissues, and microorganisms are typically observed using compound microscopes, as their thin slices allow for detailed study.
Histology Slides:
Prepared slides containing various tissues are commonly analyzed in medical and biological research.
Microbial Cultures:
Bacteria and yeast cultures are often examined to observe their shapes.
These microscopes are essential tools for researchers and students in biology and medicine.
Best Specimens for Stereo Microscopes
Stereo microscopes are best suited for observing larger, opaque specimens that require a three-dimensional view. Some suitable examples include:
Insects and Plants:
The three-dimensional perspective is beneficial for understanding the anatomy.
Mechanical Parts:
Professionals in engineering and manufacturing often use stereo microscopes to inspect small components.
Fossils and Rocks:
Geologists utilize stereo microscopes to study surface features.
With their ability to provide depth perception, stereo microscopes are invaluable for tasks requiring detailed surface examination.
Magnification Ranges of Compound Microscopes
The magnification range for compound microscopes is generally between 40x to 1000x, although some advanced models can reach up to 2000x. This range allows users to observe tiny structures in great detail, making compound microscopes essential for research in biology and medicine.
Magnification Ranges of Stereo Microscopes
Stereo microscopes generally offer a lower magnification range from 10x to 80x. While this may seem limited, it is sufficient for observing larger specimens in three dimensions. The lower magnification enables users to view the entire object and its features without losing depth perception.
Users of Compound Microscopes

Compound microscopes are primarily used by individuals who require detailed observations of small specimens. These include:
Students:
High school and college students studying biology often use compound microscopes for hands-on learning.
Researchers:
Scientists in laboratories rely on these microscopes for detailed analysis of cellular structures.
Medical Professionals:
Pathologists and healthcare professionals use compound microscopes for diagnosing diseases.
Anyone needing to study small, detailed specimens will find compound microscopes beneficial.
Users of Stereo Microscopes
Stereo microscopes are ideal for a broader audience, including:
Beginners and Hobbyists:
Those new to microscopy, such as students and hobbyists, often find stereo microscopes user-friendly.
Educators:
Teachers in biology or environmental science use stereo microscopes to demonstrate anatomy and ecology concepts.
Professionals in Various Fields:
Fields like electronics and botany often require stereo microscopes for inspecting surfaces.
The accessible design of stereo microscopes makes them suitable for users at all skill levels.
Advantages of Stereo Microscopes for Beginners
For those new to microscopy, stereo microscopes offer several benefits:
Ease of Use:
The three-dimensional view and lower magnification make it simpler to locate and observe specimens.
Wide Field of View: Stereo microscopes provide a larger field of view, allowing users to see more of the specimen at once.
Comfortable Viewing:
The design typically allows for comfortable viewing without straining the eyes.
These features encourage exploration and learning, making stereo microscopes a great starting point for anyone new to the field.
Considerations When Choosing a Microscope
When selecting a microscope, consider several key factors:
Type of Specimens:
Determine whether you need to observe small, thin specimens (compound microscope) or larger, opaque ones (stereo microscope).
Magnification Range:
Identify the magnification required for your work, as higher magnifications are needed for detailed studies.
Budget:
Microscopes vary in price, so consider your budget while looking for models that meet your requirements.
Ease of Use:
If you are a beginner, opt for models that are user-friendly and comfortable to operate.
Additional Features:
Consider adjustable lighting, camera compatibility, and ergonomic design.
By taking these factors into account, you can select the right microscope for your specific needs.
Compound Microscope vs. Stereo Microscope: Conclusion
Understanding the differences between a compound microscope vs. stereo microscope is essential for choosing the right tool to suit your needs. Whether you’re a student, researcher, or hobbyist, knowing the distinct purposes of a compound microscope vs. stereo microscope can make all the difference in your exploration of the microscopic world.
By considering the types of specimens you plan to observe, you can decide whether a compound microscope vs. stereo microscope is better suited for your tasks. Each offers unique advantages, and understanding these differences ensures you get the most out of your microscopy experience. Choosing wisely between a compound microscope vs. stereo microscope will elevate your scientific or educational pursuits.
